What Is Mostly on the RBT Exam? Your Ultimate Guide to Mastering the Test
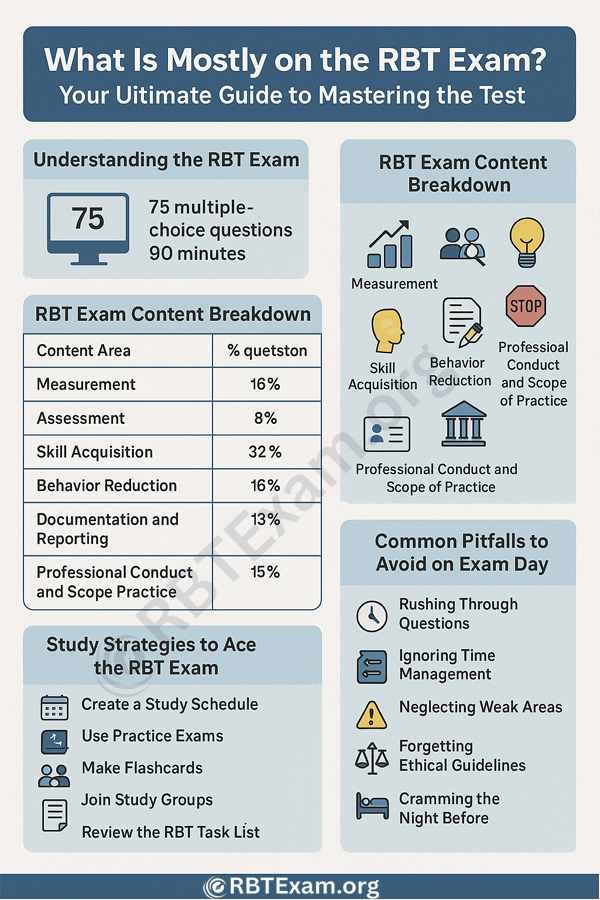
IF aiming to become registered behavior technicians, candidates must pass the Registered Behavior Technician (RBT) exam, which evaluates their capacity to apply fundamental Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) concepts. Based on the RBT Task List (2nd Edition), the test mostly addresses six key content areas: Measurement (12 questions), Assessment (6 questions), Skill Acquisition (24 questions), Behavior Reduction (12 questions), Documentation and Reporting (10 questions), and Professional Conduct and Scope of Practice (11 questions). Designed from a total of 85, these 75 multiple-choice questions test your knowledge and practical application in less than 90 minutes. Usually needing at least 68 right answers, passing requires a scaled score showing competency.
Deeply exploring every area, this guide provides a thorough analysis, study pointers, and resources to enable your success.
Effective preparation and certification achievement depend on knowing what the RBT test covers. Under administration by the Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB), this computer-based test assesses your preparedness to operate under the direction of a Board Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA) or Board Certified Assistant Behavior Analyst (BCaBA). Emphasizing ethical norms and practical knowledge, the test guarantees that you will be ready to assist individuals with autism and other developmental disabilities. With special lists and tables to direct your study path, let’s closely examine the structure, topics, and tactics of the test.
Understanding the RBT Exam: A Quick Overview
Let me establish the scene before delving into the specifics. Designed for those who have passed an initial competency test and finished a 40-hour RBT training program, the RBT exam is a standardized examination. It tests not just memorization but also your capacity to use AVA ideas in practical situations. There are just 85 multiple-choice questions in the exam—75 of which are scored—and 10 unscored pilot questions for next tests. You have 90 minutes to do it, hence you must strike a mix of speed and precision.
The content comes from the RBT Task List (2nd Edition), which lists the competencies required of an RBT. Each curriculum area will be broken down below together with study pointers and useful advice to help you get ready. Whether you have prior experience or are fresh to ABA, this book will provide you the tools to approach the test boldly.
RBT Exam Content Breakdown: What’s Tested?
There are Six topic categories covering a particular facet of behavior analysis make up the RBT test. Including percentages of the test and important subjects, here is a thorough overview of what each portion comprises.
RBT Exam Content Areas and Weighting
| Content Area | Number of Questions | Percentage of Exam | Key Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement | 12 | 16% | Data collection methods (frequency, duration, latency), graphing, and analysis |
| Assessment | 6 | 8% | Preference assessments, functional behavior assessments, client observations |
| Skill Acquisition | 24 | 32% | Discrete trial training, prompting, reinforcement, task analysis |
| Behavior Reduction | 12 | 16% | Antecedent interventions, differential reinforcement, extinction procedures |
| Documentation and Reporting | 10 | 13% | Session notes, progress reports, confidentiality, legal requirements |
| Professional Conduct and Scope of Practice | 11 | 15% | Ethical guidelines, supervision requirements, client dignity, feedback response |
This table shows that, at over one-third of the test, the largest portion is Skill Acquisition . Although it is important to concentrate on this topic, don’t ignore the other questions because each one affects your scaled score.
Deep Dive into Each Content Area
To make sure you’re ready, let’s closely examine every part including important ideas, samples, and study strategies.
1. Measurement: Tracking Behavior Accurately
Measurement in customer development is gathering and evaluating data. Using approaches like frequency (counting events), length (time spent on a behavior), and latency (time between stimulus and reaction), an RBT will If a client hand-flaps, for instance, you can note how often it occurs in a session (frequency) or the length of each episode (duration).
Key Concepts to Master:
- Continuous vs. Discontinuous Measurement: Continuous methods (e.g., event recording) track every instance, while discontinuous methods (e.g., partial interval recording) sample behavior and may overestimate frequency.
- Graphing Data: Understand how to plot data points to visualize trends.
- Data Analysis: Identify patterns to evaluate intervention effectiveness.
Study Tip: Using situations, practice differentiating between measuring techniques. For example, “Max counts how often a client pinches herself in 30 minutes.” That frequency recording is what you have here. Make flash cards for terms like “latency” and “interobserver agreement.”
2. Assessment: Understanding Client Needs
The part on assessments evaluates your capacity to help determine clients. Although most assessments are handled by BCBAs, RBTs assist in activities such preference assessments—identifying reinforcers—or watching behaviors for functional behavior assessments—FBAs.
Key Concepts to Master:
- Preference Assessments: Methods like paired-choice or multiple stimulus without replacement (MSWO) to identify client preferences.
- Functional Behavior Assessments: Observing behaviors to determine their function (e.g., attention-seeking, escape).
- Client Observations: Noting environmental factors that influence behavior.
Study Tip: To learn about assessment activities, see the RBT Task List. Exercises include “You present two items to a client and record which they choose.” That is a preference evaluation using paired choices.
3. Skill Acquisition: Teaching New Behaviors
Examining strategies to teach clients new abilities, including communication or daily life chores, the portion on skill acquisition is the largest in the test. Ask about discrete trial training (DTT), natural environment training (NETT), and task analysis—that is, breaking up abilities into phases.
Key Concepts to Master:
- Discrete Trial Training (DTT): Structured teaching with clear prompts, responses, and consequences.
- Prompting and Fading: Using cues (e.g., verbal, physical) to guide behavior and gradually removing them.
- Reinforcement: Positive (adding a reward) vs. negative (removing an aversive stimulus) reinforcement to encourage behavior.
Study Tip: Memorize the steps of DTT: discriminative stimulus, prompt, reaction, consequence, intertrial interval—memory. Use them in situations like teaching a youngster to speak “ball” using cues.
4. Behavior Reduction: Managing Challenging Behaviors
Behavior reduction is mostly concerned with techniques to cut maladaptive habits like self-injury or hostility. To support good alternatives, you will have to know how to change antecedents (triggers) and consequences.
Key Concepts to Master:
- Antecedent Interventions: Changing the environment to prevent behaviors (e.g., reducing demands to avoid escape behaviors).
- Differential Reinforcement: Reinforcing desired behaviors while withholding reinforcement for undesired ones (e.g., DRA, DRO).
- Extinction: Stopping reinforcement to reduce a behavior’s occurrence.
Study Tip: Make a chart comparing DRA, DRO, DRI, DRL forms of differential reinforcement. Differential reinforcement of alternative behaviour (DRA), for instance, rewards a substitute behavior—that of applauding a youngster for raising their hand rather than yelling.
5. Documentation and Reporting: Keeping Accurate Records
Documentation and Reporting assures client anonymity and helps you to capture session data confidentiality. This part evaluates your legal and occupational standards compliance as well as your ability to create session notes and progress reports.
Key Concepts to Master:
- Session Notes: Objective descriptions of what occurred during a session.
- Confidentiality: Following HIPAA and BACB guidelines to protect client information.
- Progress Reports: Summarizing client progress for BCBAs and caregivers.
Study Tip: Create scenario-based example session notes for your own writing. In a 20-minute session, for instance, “Client engaged in 3 instances of hand-flapping, reduced from 5 last week.” Review documentation requirements with a study guide.
Resource: For more on documentation, explore this RBT Study Guide for practical examples.
6. Professional Conduct and Scope of Practice: Ethical Practice
Professional Conduct examines your knowledge of ethical standards, monitoring criteria, and client dignity preservation. You will be asked about how you responded to comments, stayed within your purview, and followed the RBT Ethics Code (2.0).
Key Concepts to Master:
- RBT Ethics Code: Guidelines on boundaries, confidentiality, and professionalism.
- Supervision Requirements: RBTs must receive ongoing supervision from a BCBA or BCaBA.
- Client Dignity: Respecting clients’ rights and preferences.
Study Tip: Learn important RBT Ethics Code principles by heart; they are available on the BACB website. “If a client’s family asks you to diagnose a behaviour, what do you do?” practice scenario-based questions ask. (Answer: See the BCBA; diagnosis is outside the purview of an RBT.)
Study Strategies to Ace the RBT Exam
Getting ready for the RBT exam calls both organization and methodologies. These are doable plans to optimize your study time:
Top 5 Study Tips for the RBT Exam
- Create a Study Schedule: Dedicate 1–2 hours daily over 4–6 weeks, focusing on one content area per session. For example, study Measurement on Mondays and Skill Acquisition on Tuesdays.
- Use Practice Exams: Take mock tests to simulate exam conditions and identify weak areas. Time yourself to practice pacing (roughly 1 minute per question).
- Make Flashcards: Write key terms and definitions (e.g., “What is extinction?”) on flashcards. Organize them by content area for targeted review.
- Join Study Groups: Collaborate with peers to discuss concepts and quiz each other. This reinforces understanding through teaching.
- Review the RBT Task List: Download the Task List from the BACB website and ensure you understand each item. It’s the exam’s blueprint.
Resource: Try a 75-question RBT practice test to gauge your readiness.
Recommended Study Resources
| Resource Type | Description | Where to Find |
|---|---|---|
| RBT Task List | Official list of skills and knowledge tested on the exam | BACB website |
| Practice Exams | Mock tests with 75–85 questions to simulate the real exam | rbtexam.org, Mometrix, Test-Guide.com |
| Flashcards | Digital or physical cards for memorizing terms and concepts | Quizlet, RBT Exam Study Guide books |
| Study Guides | Comprehensive books with explanations and practice questions | Amazon, rbtexam.org |
| YouTube Videos | Free tutorials breaking down the RBT Task List and scenarios | Search “RBT Exam Prep” on YouTube |
For high-quality practice questions, check out RBTExam.Org Free RBT Practice Exam for instant feedback.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid on Exam Day
Even with thorough preparation, small mistakes can trip you up. Here’s how to stay on track:
5 Common RBT Exam Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Rushing Through Questions: Read each question carefully to avoid misinterpreting scenarios. If unsure, mark it and return later.
- Ignoring Time Management: Allocate about 1 minute per question. Practice with timed mock exams to build speed.
- Neglecting Weak Areas: Don’t focus only on strengths like Skill Acquisition. Use practice tests to identify and study weaker sections like Assessment.
- Forgetting Ethical Guidelines: Review the RBT Ethics Code to handle questions about professional conduct confidently.
- Cramming the Night Before: Study consistently over weeks to retain information. Get a good night’s sleep before the exam.
Real-World Application: Why the RBT Exam Matters
Taking the RBT exam is about becoming ready to change customers’ life, not only about obtaining a certification. Working directly with people—often children with autism—you, an RBT, will help them to increase their communication, social skills, and independence. For instance, I once met with an RBT who described how learning to use image cards—a life-changing event for the family—how mastering Skill Acquisition techniques enabled a nonverbal youngster learn to request objects.
The test ensures your readiness to manage these obligations ethically and successfully. Working under a BCBA’s direction, you may produce significant change by knowing ideas like reinforcement and behavior modification.
Learn more about ABA therapy’s impact on autism from the Autism Speaks website.
Exam Day Tips: Setting Yourself Up for Success
When the big day arrives, stay calm and focused. Here are practical tips to shine:
5 Exam Day Must-Dos
- Arrive Early: Get to the Pearson VUE testing center 15–30 minutes early with a valid photo ID.
- Bring Minimal Items: Leave personal items at home or in a locker, as they’re not allowed in the testing room.
- Stay Calm: If you feel anxious, take deep breaths or close your eyes for a moment during the exam.
- Read Carefully: Pay attention to scenario-based questions, as they often test application over rote memorization.
- Review Answers: If time allows, double-check your responses, especially for tricky ethical or assessment questions.
FAQs
Q. What topics are most commonly covered on the RBT exam?
The RBT test mostly tests fundamental topics like measurement, evaluation, skill development, behavior modification, documentation and reporting, and professional ethics. Usually, the most inquiries include behavior modification and skill development.
Q. How many questions do I need to get right to pass the RBT exam?
There are 85 questions total on the RBT test—75 scored and 10 unscored pilot questions. Although the passing score is not publicly revealed, it is thought that passing requires answering about 60–65 questions correctly (80–85%).
Q. What is the best way to study for the RBT exam?
Using RBT practice tests, flashcards, ABA terminology guides, and emphasizing task list ideas is the best approach to study. Examining real-life situations and applying visual tools like flow charts and infographics helps many applicants discover success.
Q. How difficult is the RBT exam for first-time test takers?
The challenges change depending on preparedness. Most applicants find the test under control with organized preparation and practice. If first-timers are not familiar with practical applications, however, they might find ABA jargon or scenario-based questions difficult.
Q. Are there any trick questions on the RBT exam?
Although there are no “trick” questions, some are purposefully written to challenge your grasp of subtle ABA ideas. Pay particular attention to concepts requiring critical thought such “most appropriate,” “least intrusive,” and “ethical response.”
Final Thoughts: Your Path to RBT Certification
A demanding but reasonable path towards a fulfilling career in behavior analysis is the RBT test. Concentrating on the six topic areas—Measurement, Assessment, Skill Acquisition, Behavior Reduction, Documentation and Reporting, and Professional Conduct—you will approach the test with assurance. Your route map is the RBT Task List; practice with simulated tests; rely on study materials and flashcards to reinforce important ideas. Having a disciplined study schedule and appropriate tools will help you to pass the test and begin having a positive influence as a Registered Behavior Technician.
All set to go forward? Use the resources suggested to start your preparation; never hesitate to contact study groups or mentors for help. You really have it.






